Standard Data Types
A variable can hold different types of values. For example, a person's name must be stored as a string whereas its id must be stored as an integer.
Python provides various standard data types that define the storage method on each of them. The data types defined in Python are given below.
- Numbers
- Sequence Type
- Boolean
- Set
- Dictionary
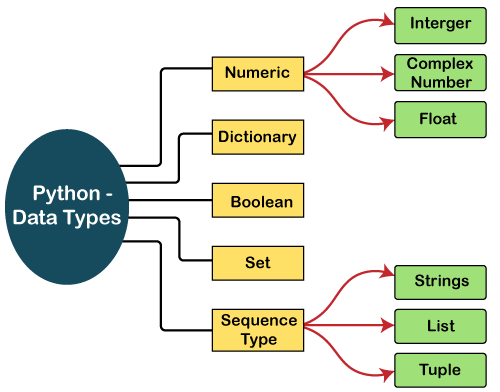
In this section of the tutorial, we will give a brief introduction of the above data-types. We will discuss each one of them in detail later in this tutorial.
Numbers
Number stores numeric values. The integer, float, and complex values belong to a Python Numbers data-type. Python provides the type() function to know the data-type of the variable. Similarly, the isinstance() function is used to check an object belongs to a particular class.
Python supports three types of numeric data.
- Int - Integer value can be any length such as integers 10, 2, 29, -20, -150 etc. Python has no restriction on the length of an integer. Its value belongs to int
- Float - Float is used to store floating-point numbers like 1.9, 9.902, 15.2, etc. It is accurate upto 15 decimal points.
- complex - A complex number contains an ordered pair, i.e., x + iy where x and y denote the real and imaginary parts, respectively. The complex numbers like 2.14j, 2.0 + 2.3j, etc.
Sequence Type
String
The string can be defined as the sequence of characters represented in the quotation marks. In Python, we can use single, double, or triple quotes to define a string.
String handling in Python is a straightforward task since Python provides built-in functions and operators to perform operations in the string.
In the case of string handling, the operator + is used to concatenate two strings as the operation "hello"+" python" returns "hello python".
Tuple
A tuple is similar to the list in many ways. Like lists, tuples also contain the collection of the items of different data types. The items of the tuple are separated with a comma (,) and enclosed in parentheses ().
A tuple is a read-only data structure as we can't modify the size and value of the items of a tuple.
Dictionary
Dictionary is an unordered set of a key-value pair of items. It is like an associative array or a hash table where each key stores a specific value. Key can hold any primitive data type, whereas value is an arbitrary Python object.
Boolean
Boolean type provides two built-in values, True and False. These values are used to determine the given statement true or false. It denotes by the class bool. True can be represented by any non-zero value or 'T' whereas false can be represented by the 0 or 'F'.
Set
Python Set is the unordered collection of the data type. It is iterable, mutable(can modify after creation), and has unique elements. In set, the order of the elements is undefined; it may return the changed sequence of the element. The set is created by using a built-in function set(), or a sequence of elements is passed in the curly braces and separated by the comma. It can contain various types of values.



0 Comments