What is the Internet?
The internet is a global system which use TCP/IP protocol suite to link various types of electric devices worldwide. The internet is a collection of interconnected devices which are spread across the globe. It is a network of networks that consist of public, private, public, sales, finance, academic, business and government networks. The internet is a type of network and called network of networks.
What is World Wide Web?
World Wide Web, which is also known as a Web, is a collection of websites or web pages stored in web servers and connected to local computers through the internet. These websites contain text pages, digital images, audios, videos, etc. Users can access the content of these sites from any part of the world over the internet using their devices such as computers, laptops, cell phones, etc. The WWW, along with internet, enables the retrieval and display of text and media to your device.
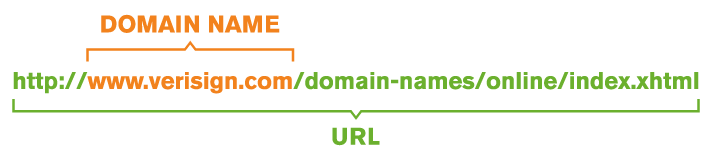
What is a URL?
Is a URL the same as a domain name? Surprisingly to many, the answer is no. But the terms are used so interchangeably, it’s understandable why people confuse one for the other. But there is a difference.
A domain name is part of a URL, which stands for Uniform Resource Locator. You can see the visual difference in the following example:
IP addresses
An IP address is a number identifying of a computer or another device on the Internet. It is similar to a mailing address, which identifies where postal mail comes from and where it should be delivered. IP addresses uniquely identify the source and destination of data transmitted with the Internet Protocol.
IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long (four bytes). An example of an IPv4 address is 216.58.216.164, which is the front page of Google.com.
IP address classes
With an IPv4 IP address, there are five classes of available IP ranges: Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D and Class E, while only A, B, and C are commonly used. Each class allows for a range of valid IP addresses, shown in the following table.
|
Class |
Address
range |
Supports |
|
Class A |
1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254 |
Supports 16 million hosts on each of 127
networks. |
|
Class B |
128.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254 |
Supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000
networks. |
|
Class C |
192.0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254 |
Supports 254 hosts on each of 2 million
networks. |
|
Class D |
224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 |
Reserved for multicast groups. |
|
Class E |
240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254 |
Reserved for future use, or research and
development purposes. |
ISP (Internet service provider)
Alternatively known as an access provider or network provider, an ISP (Internet service provider) is a company that provides Internet access to users or subscribers of its service. An ISP gives you an Internet account (access to the Internet), e-mail address, web space for a web page for around $20.00 U.S. dollars a month. Prices may vary in other countries.
List of major ISPs
- AT&T
- CenturyLink (formerly Qwest).
- Cox Cable
- Google Fiber
- Sparklight (formerly Cable One).
- Spectrum /Charter Communications (formerly Time Warner Cable).
- Windstream (which includes Earthlink).
- Verizon
- Xfinity (formerly Comcast).
IMEI
IMEI, also known as International Mobile Station Equipment Identity, is a number used to identify certain types of 3GPP mobile and satellite phones. It is usually printed inside the battery compartment, or accessed when the phone is powered on by dialing *#06#. On smartphones, it's found in most operating sys





0 Comments