Python Exception
An exception can be defined as an unusual condition in a program resulting in the interruption in the flow of the program.
Whenever an exception occurs, the program stops the execution, and thus the further code is not executed. Therefore, an exception is the run-time errors that are unable to handle to Python script. An exception is a Python object that represents an error
Python provides a way to handle the exception so that the code can be executed without any interruption. If we do not handle the exception, the interpreter doesn't execute all the code that exists after the exception.
Python has many built-in exceptions that enable our program to run without interruption and give the output. These exceptions are given below:
Common Exceptions
Python provides the number of built-in exceptions, but here we are describing the common standard exceptions. A list of common exceptions that can be thrown from a standard Python program is given below.
- ZeroDivisionError: Occurs when a number is divided by zero.
- NameError: It occurs when a name is not found. It may be local or global.
- IndentationError: If incorrect indentation is given.
- IOError: It occurs when Input Output operation fails.
- EOFError: It occurs when the end of the file is reached, and yet operations are being performed.
Exception handling in python
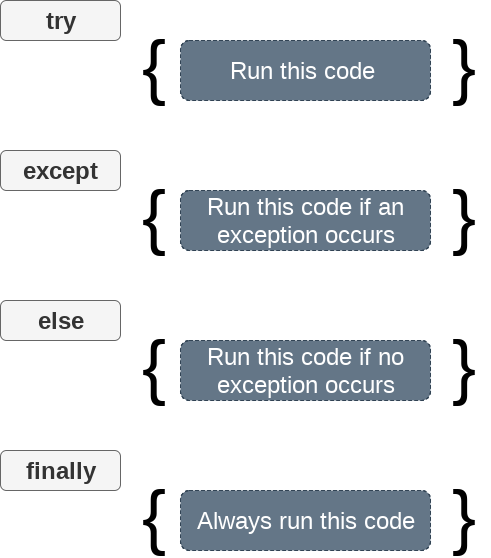
The try-expect statement
If the Python program contains suspicious code that may throw the exception, we must place that code in the try block. The try block must be followed with the except statement, which contains a block of code that will be executed if there is some exception in the try block.

Declaring Multiple Exceptions
The Python allows us to declare the multiple exceptions with the except clause. Declaring multiple exceptions is useful in the cases where a try block throws multiple exceptions.
The try...finally block
Python provides the optional finally statement, which is used with the try statement. It is executed no matter what exception occurs and used to release the external resource. The finally block provides a guarantee of the execution.
We can use the finally block with the try block in which we can pace the necessary code, which must be executed before the try statement throws an exception.



0 Comments