Python List
A list in Python is used to store the sequence of various types of data. Python lists are mutable type its mean we can modify its element after it created. However, Python consists of six data-types that are capable to store the sequences, but the most common and reliable type is the list.
A list can be defined as a collection of values or items of different types. The items in the list are separated with the comma (,) and enclosed with the square brackets [].
Characteristics of Lists
The list has the following characteristics:
- The lists are ordered.
- The element of the list can access by index.
- The lists are the mutable type.
- The lists are mutable types.
- A list can store the number of various elements.
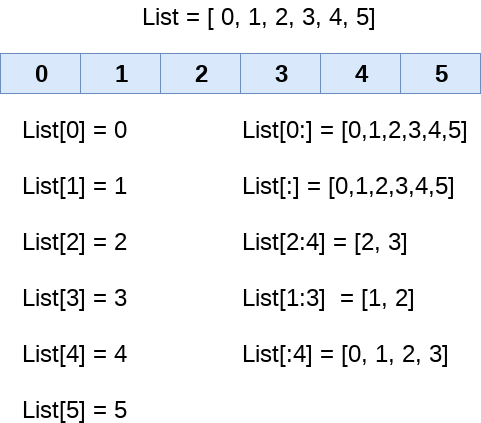
List indexing and splitting
The indexing is processed in the same way as it happens with the strings. The elements of the list can be accessed by using the slice operator [].
The index starts from 0 and goes to length - 1. The first element of the list is stored at the 0th index, the second element of the list is stored at the 1st index, and so on.
Python
List Operations
The concatenation (+) and repetition (*) operators work in the
same way as they were working with the strings.
Let's see how the list responds to various operators.
1.
Consider a Lists l1 = [1, 2, 3, 4], and l2 = [5, 6, 7, 8] to perform operation.
|
Operator |
Description |
Example |
|
Repetition |
The repetition operator enables the list elements to be repeated
multiple times. |
L1*2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4] |
|
Concatenation |
It
concatenates the list mentioned on either side of the operator. |
l1+l2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] |
|
Membership |
It returns true if a particular item exists in a particular list
otherwise false. |
print(2 in l1) prints True. |
|
Iteration |
The
for loop is used to iterate over the list elements. |
for i in l1: print(i)
Output 1234 |
|
Length |
It is used to get the length of the list |
len(l1) = 4 |
Python
List Built-in functions
Python provides the following built-in functions, which can be
used with the lists.
|
SN |
Function |
Description |
Example |
|
1 |
cmp(list1, list2) |
It compares the elements of both the lists. |
This method is not used in the Python 3 and the above versions. |
|
2 |
len(list) |
It is
used to calculate the length of the list. |
L1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]print(len(L1)) 8 |
|
3 |
max(list) |
It returns the maximum element of the list. |
L1 = [12,34,26,48,72]print(max(L1))72 |
|
4 |
min(list) |
It
returns the minimum element of the list. |
L1 = [12,34,26,48,72]print(min(L1))12 |
|
5 |
list(seq) |
It converts any sequence to the list. |
str = "Johnson"s = list(str)print(type(s))<class list> |



0 Comments