Python Loops
The flow of the programs written in any programming language is sequential by default. Sometimes we may need to alter the flow of the program. The execution of a specific code may need to be repeated several numbers of times.
For this purpose, The programming languages provide various types of loops which are capable of repeating some specific code several numbers of times. Consider the following diagram to understand the working of a loop statement.
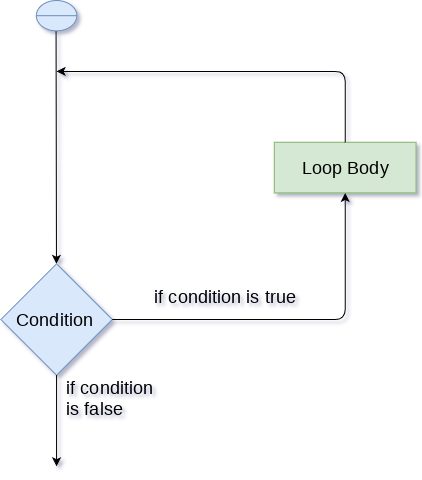
Python Loops
Advantages
of loops
There are the following advantages of loops in Python.
- It
provides code re-usability.
- Using
loops, we do not need to write the same code again and again.
- Using
loops, we can traverse over the elements of data structures (array or
linked lists).
There are the following loop statements in Python.
|
Loop
Statement |
Description |
|
for loop |
The for loop is used in the case where we need to execute some
part of the code until the given condition is satisfied. The for loop is also
called as a per-tested loop. It is better to use for loop if the number of
iteration is known in advance. |
|
while loop |
The
while loop is to be used in the scenario where we don't know the number of
iterations in advance. The block of statements is executed in the while loop
until the condition specified in the while loop is satisfied. It is also
called a pre-tested loop. |
|
do-while loop |
The do-while loop continues until a given condition satisfies.
It is also called post tested loop. It is used when it is necessary to
execute the loop at least once (mostly menu driven programs). |



0 Comments